This Site Is A Participant In The Amazon Services LLC Associates Program. We may earn money or products from Amazon or the companies mentioned in this post.
Acne is a common skin condition that occurs when the hair follicles become plugged with oil and dead skin cells. Folliculitis is a condition in which the hair follicles are inflamed. Both conditions can occur on the face, chest, back, or other areas of the body.
Treatment for acne and folliculitis may include over-the-counter medications, prescription medications, or home remedies.
Fungal acne (Malassezia folliculitis) versus Comedonal acne
Acne or folliculitis is a very common skin condition that can be very frustrating. There are many possible causes of acne, but the most common cause is an excess of oil production by the sebaceous glands. This can be due to hormonal changes, such as during puberty, or it can be a result of certain medications, such as birth control pills.
Folliculitis is an inflammation of the hair follicles that can also be caused by an excess of oil production. Treatment for acne or folliculitis typically involves cleansing the skin with mild soap and water and using over-the-counter topical medications, such as benzoyl peroxide cream. In some cases, oral antibiotics may also be necessary to clear the infection.
Folliculitis on Face
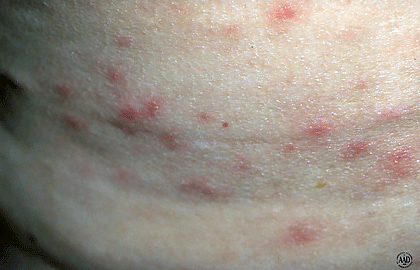
Folliculitis is a common skin condition that causes small red bumps to form around the hair follicles. The bumps may be filled with pus or contain a hard center. They can occur on any part of the body, but are most commonly found on the face, scalp, chest, and back.
Folliculitis is usually caused by a bacterial or fungal infection. However, it can also be triggered by physical irritation, such as shaving or tight clothing. In some cases, an underlying medical condition may be to blame.
Most cases of folliculitis are mild and clear up on their own within a few days. However, more severe cases may require treatment with antibiotics or antifungal medications. In rare cases, permanent scarring can occur.
Pityrosporum Folliculitis
Pityrosporum Folliculitis is a fungal acne causing inflammation of the hair follicles. The fungus responsible for this condition is called Malassezia. This fungus is found on the skin surface and feeds off of sebum, which is an oily substance produced by the sebaceous glands.
When there is an overgrowth of this fungus, it can cause pityrosporum folliculitis.
Symptoms of pityrosporum folliculitis include small red bumps on the skin that may be itchy or painful. The bumps are often filled with pus and may crust over.
They are usually found on the chest, back, shoulders, or face. In severe cases, the bumps can spread to other areas of the body such as the arms and legs.
Treatment for pityrosporum folliculitis typically includes anti-fungal medications that are applied to the skin or taken orally.
In some cases, a course of oral steroids may also be prescribed to help reduce inflammation. In severe cases, isotretinoin may be necessary to control the condition.
Folliculitis Treatment
If you have folliculitis, you know how annoying and painful it can be. The good news is that there are a number of treatment options available to help you get rid of the infection and get back to your normal self.
Folliculitis is an infection of the hair follicles that can occur on any part of the body where hair grows.
The most common areas affected are the face, scalp, chest, back, and buttocks. The infection is usually caused by bacteria or fungi that enter the skin through cuts or other breaks in the skin. It can also be caused by shaving or wearing tight clothing that doesn’t allow the skin to breathe.
Symptoms of folliculitis include small red bumps around the hair follicles, itching, burning, and pain. In some cases, the bumps may fill with pus or bleed. If the infection spreads to deeper layers of skin, it can cause larger bumps called abscesses.
Abscesses are usually more painful than folliculitis and may need to be drained by a doctor.
There are a number of over-the-counter treatments available for folliculitis. These include creams and ointments containing antibiotics or antifungals such as miconazole or clotrimazole .
You can also try using a warm compress on the affected area for 10-15 minutes several times a day. If these treatments don’t work, your doctor may prescribe oral antibiotics or antifungals . In severe cases, surgery may be necessary to remove infected hair follicles .
With proper treatment , most cases of folliculitis will clear up within two weeks . However , some types of fungus can cause recurrent infections . If your infections keep coming back , talk to your doctor about other treatment options such as laser therapy .
Strongest Antibiotic for Folliculitis
Folliculitis is a skin condition that results when the hair follicles are inflamed. It can be caused by a number of different things, including bacteria, viruses, and fungi. Treatment for folliculitis depends on the underlying cause, but often includes antibiotics.
The strongest antibiotic for folliculitis will depend on the specific bacteria or other organism that is causing the infection. For example, if Staphylococcus aureus is the culprit, then an antibiotic like methicillin or vancomycin may be prescribed. If Pseudomonas aeruginosa is responsible, then an antibiotic like ciprofloxacin or levofloxacin may be recommended.
The decision about which antibiotic to use should be made by a doctor after taking into account the specific circumstances of each case.
Fungal Folliculitis
Fungal folliculitis is a fungal infection of the hair follicles. It can occur on any part of the body, but is most common on the scalp, face, chest and back. The fungus that causes this condition is called Malassezia.
Fungal folliculitis often starts as an itchy rash with small red bumps. The bumps may then fill with pus and crust over. In severe cases, the hair follicles may become inflamed and infected.
This can lead to hair loss. Fungal folliculitis is not contagious and can usually be treated with antifungal creams or shampoos. However, if the infection spreads or does not respond to treatment, you may need oral antifungals or other medications.
Credit: www.aad.org
Do I Have Folliculitis Or Acne?
There are a few key ways to tell the difference between folliculitis and acne. First, look at the location of the breakouts. Folliculitis typically occurs on the face, neck, chest, back, buttocks, and legs—basically anywhere you have hair follicles.
Acne breakouts can occur anywhere on the body but are most common on the face, chest, shoulders, and back. Second, take a close look at the breakouts themselves. Folliculitis bumps tend to be small red or white pus-filled pimples that surround hair follicles.
They may also be itchy or painful. Acne breakouts can vary in size from tiny blackheads to large cysts and usually don’t involve pus unless they’ve become infected. Finally, consider any other symptoms you might be experiencing.
Folliculitis is often accompanied by itchiness or pain around the affected area.
Can Folliculitis Be Mistaken for Acne?
Folliculitis is a skin condition that results when the hair follicles become inflamed. The inflammation can be caused by a variety of things, including bacteria, yeast, or fungus. Folliculitis most often appears as small red bumps on the skin.
It can occur on any part of the body, but is most common on the face, scalp, chest, and back. Acne is also a skin condition that results in red bumps on the skin. However, acne is caused by excess oil and dead skin cells clogging the pores.
Acne can also occur on any part of the body, but is most common on the face, chest, and back. While folliculitis and acne may both result in red bumps on the skin, they are two different conditions with different causes.
How Long Do Folliculitis Pimples Last?
Folliculitis is a skin condition that results when the hair follicles become inflamed. The condition can occur anywhere on the body, but is most common on the face, scalp, chest, and back. Folliculitis often appears as small red bumps or white-headed pimples around the hair follicles.
It is usually not painful or itchy, but it can sometimes lead to more serious infections.
Most cases of folliculitis are mild and clear up on their own within a few days to weeks. However, some types of folliculitis may require treatment with antibiotics or other medications.
In rare cases, folliculitis can spread to other parts of the body and cause serious complications.
What Does a Folliculitis Bump Look Like?
A folliculitis bump is a small, red, raised bump that appears on the skin. It is often itchy and may be painful. The bump is caused by inflammation of the hair follicle.
Folliculitis bumps can occur on any part of the body where there is hair, but they are most common on the face, scalp, chest, back, and buttocks.
Conclusion
Acne or folliculitis can be a difficult decision for many people. Both are skin conditions that can be very uncomfortable and cause a lot of embarrassment. Acne is caused by a build-up of sebum, which is an oily substance produced by the body.
This build-up clogs pores and hair follicles, which then become inflamed and cause pimples or blackheads. Folliculitis, on the other hand, is an infection of the hair follicles that can be caused by bacteria, fungi, or even an ingrown hair. The symptoms of folliculitis include redness, itching, burning, and bumps around the hair follicles.
It is important to see a doctor if you think you may have either acne or folliculitis so they can properly diagnose and treat the condition.